A Turbine for Your Hot Rod? Latham Says Yes
Supercharging has interesting roots (pun intended) in the automotive world. The idea of pressure-feeding air into an engine for a car is only a few years younger than the automobile itself. The first production examples were available on Mercedes models in 1922, and it has only become more popular since. As with many examples of technology, there were some interesting attempts at supercharging that didn’t last and ended up on the side of the long road that is automotive history. One such example is the Latham axial flow supercharger.

Supercharging an engine relies on the crankshaft to drive on a compressor that forces air into the intake, effectively increasing the volumetric efficiency of the engine by cramming more air into the cylinders than it would pull in on its own during the vacuum created by the intake stroke. The most common forms of superchargers are centrifugal, roots, screw, and scroll. Before the market settled on the common types we’re familiar with today, there were several efforts to create the next best thing. Norman Latham of West Palm Beach, Florida, hoped his new product would be a must-have performance bolt-on.
Latham’s idea was to create an axial supercharger. This is essentially a turbine, where the supercharger housing contains “fans” that can create positive manifold pressure. Latham’s design went into production in 1956 and was sold until 1965. It was radically different than a roots or centrifugal supercharger, yet also combined a few of the better parts of each. A centrifugal supercharger was a bear to tune 70 years ago because carburetors were still the most popular way of mixing the air and fuel entering an engine.

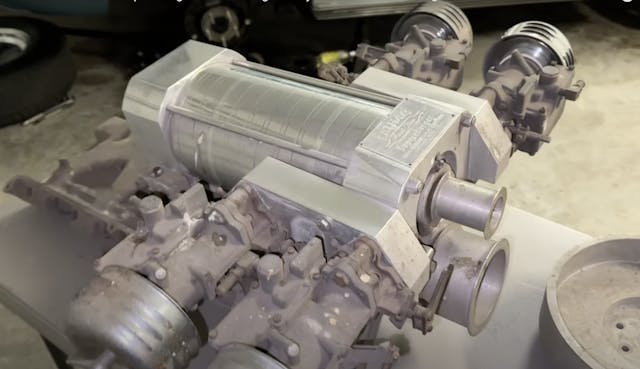
Carburetors rely on the incoming air to pull in the fuel into the airstream from the float bowl. If the throat of the carburetor is under pressure rather than vacuum, that fuel draw doesn’t work very well. This made centrifugal superchargers finicky. Roots-style blowers could more effectively be set up to draw air through carburetors, but the size and location made packaging tough. Latham used the long and low design of the axial supercharger to put the blower low and further forward with the carbs off to the side, keeping a lower profile. The air and fuel are drawn in through two or four carbs, depending on the model, before being compressed through the turbine and then fed into the intake manifold.

The problem is that axial compressors tend to be less efficient than the more popular styles of supercharging. Their peak efficiency orrurs during a very narrow window and prefer steady-state running at that speed rather than changing RPM quickly like most automotive engines tend to do. It was a solution, but we know now that it was not the best solution.
The design still caught people’s attention though. After an eight-page spread in the June 1956 issue of Hot Rod things seemed to take off. Over 600 Latham superchargers were built and are now highly sought after. The company was sold in 1982 and transitioned to producing a modern interpretation of the axial design. The vintage units stand as an interesting reminder of the times when its innovation was almost as rapid as the cars it was going into.
***
Check out the Hagerty Media homepage so you don’t miss a single story, or better yet, bookmark it. To get our best stories delivered right to your inbox, subscribe to our newsletters.



This kind of stuff is the cool stuff to have.
The show I went to this weekend had 20 cars with superchargers and they all were the same unit.
I like the dare to be different.
Very interesting article, but an explanation of how the different types of superchargers WORK, would be of great value.
Never seen that type before. it is very cool. Still spinning just fine after all these years.